Cisco MC3810s in a Typical Network
Interfaces and Service Capabilities
Physical Ports
Administrative Interface Ports
BRI S/T Backup Port
The Cisco MC3810 series multiservice access concentrator integrates data, voice/fax, and video signals and connects them to Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM), Frame Relay, or leased-line networks.
Through its various ports, the Cisco MC3810 series concentrator can support a variety of network and user interfaces, including T1/E1 trunks, serial data ports, an Ethernet LAN connection, private branch exchanges (PBXs), telephone key systems, analog telephones, and Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN) Basic Rate Interface (BRI) services.
Five basic hardware variations of Cisco MC3810 series concentrators are available, based on the choice of optional modules. All five chassis variations are equipped with two serial data ports, one Ethernet 10BaseT port, and two administrative ports.
| Note Certain releases of Cisco IOS software do not support the video codec dialing interface. |
Figure 1-1 through Figure 1-5 show typical examples of the five chassis variations.
Cisco MC3810 series concentrators support routing between their various data ports, and they support transparent bridging per Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC) 802.1d and IEEE 802.1d specifications. They can be optionally equipped to support redundancy backup of their wide-area network (WAN) interface ports. Redundancy backup is provided by an optional ISDN BRI port that can be programmed for automatic switchover. This port has an ISDN S/T interface, and this function is referred to here as BRI S/T backup.
You can place a Cisco MC3810 series concentrator on a desktop, or you can mount it in a 19- or 24-inch rack or on a wall.
Figure 1-1: Cisco MC3810 with Base
Chassis
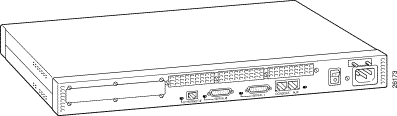
Figure 1-2: Cisco MC3810 with Analog
Voice Ports
Figure 1-3: Cisco MC3810 with Digital
Voice Port, T1/E1 Trunk Port, and BRI S/T Backup Port
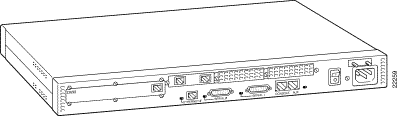
Figure 1-4: Cisco MC3810 with BRI Voice
Ports, T1/E1 Trunk Port, and BRI S/T Backup Port
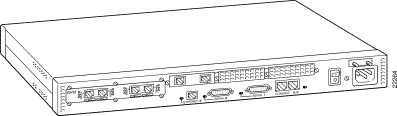
Figure 1-5: Cisco MC3810 with T1/E1
Trunk Port and Video Dialing Module
Figure 1-6 shows how Cisco MC3810 series concentrators might be deployed in a typical network.
Figure 1-6: Examples of Possible Deployment Scenarios
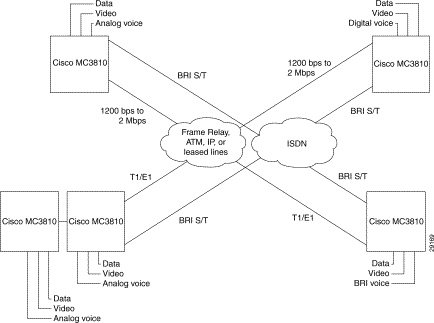
Table 1-1: Cisco MC3810 Interfaces and Service Capabilities | ||||
| Port | Interface Configurations | Interface To | Services Supported | Details |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Console | EIA/TIA-232 asynchronous serial (DCE1) | ASCII terminal Personal computer |
Local administrative access | RJ-45 physical interface |
| Auxiliary | EIA/TIA-232 asynchronous serial (DTE2) | Modem | Remote administrative access Data backup |
RJ-45 physical interface |
| Ethernet | 10BaseT (802.3) | LAN | Data | RJ-45 physical interface |
| S0 and S1 (serial) | HDLC-based data | WAN, carrier network, or user equipment |
Frame Relay Cisco HDLC PPP |
Physical interfaces:
|
| Bit-transparent mode | User equipment (video codec for example) | Nx56k or Nx64k Clear channel transport |
||
| T1/E1 trunk (MFT3) |
Channelized T1/E1 | WAN, carrier network, or user equipment |
Service types:
Transport types:
|
Built-in CSU/DSU7 T1.403-compliant Physical interfaces:
|
| BRI S/T backup (BRI 0 S/T) | ISDN BRI S/T | ISDN switch ISDN exchange |
Redundancy backup of T1/E1 trunk, serial 0, and serial 1 ports | Requires external NT18 to provide ISDN
U interface CB-1D physical interface |
| BRI voice (BVM9) |
ISDN QSIG10 BRI (ISDN 2b+d) |
PINX11 | Voice or fax | QSIG over BRI with CB-1D physical interfaces Requires installed MFT |
Analog voice (AVM12)
|
FXS | Analog phone or fax (2-wire) Key system (2-wire or 4-wire) |
Analog voice or fax | Provides battery RJ-11 physical interface |
| FXO | Central office trunk | Analog voice or fax | Receives battery RJ-11 physical interface |
|
| E&M | Analog PBX (2-wire or 4-wire) | Analog voice or fax | RJ-1CX physical interface | |
| T1/E1 digital voice (DVM13) |
T1/E1 with CAS14 | Digital PBX | Voice or fax | Voice port types:
Balanced (RJ-48) or unbalanced (coaxial) physical interface |
ISDN QSIG PRI:
|
Digital PBX | Voice or fax | ||
| Channelized T1/E1 | Digital PBX, channel bank, or video codec | Nx56k or Nx64k | ||
| Video codec dialing (VDM)18 | 2-way RS-366 control signals | Video codec (DTE) | Automatic dialing of video codecs across ATM network | Provides ACE (Automatic Calling Equipment) port in DCE mode RS-366 physical interface |
A Cisco MC3810 series concentrator has two physical ports for administrative access to the software:
An Ethernet 10BaseT interface is standard on all Cisco MC3810 series concentrators. The Ethernet port uses an RJ-45 connector for its LAN interface.
All Cisco MC3810 concentrators have two synchronous serial ports, also known as universal input/output (UIO) serial ports. The UIO serial ports can be connected either to a carrier's leased lines or to a user's synchronous serial data interfaces. They are not channelized and do not support TDM trunk services. The UIO serial ports support Frame Relay, HDLC, and PPP services. Both ports require external CSU/DSU equipment.
Each UIO serial port uses its own DB-60 connector and supports the following physical layer specifications:
The characteristics of the UIO ports---their physical layer specification and their operation as DTE or DCE---are determined by the choice of the Cisco serial cable used between the DB-60 connector and the external equipment.
Serial port 1 is subject to the following restrictions:
| Note Use the show version command to determine the processor revision in your Cisco MC3810 chassis. |
Table 1-2: Serial Port 1 Speed Limitations | |||||
| MFT | DVM | BVM | DVM Set for QSIG | ISDN BRI Backup Active | Serial Port 1 Maximum Speed1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Present | Present | - | Yes | No | 192 kbps |
| - | No | Yes | 192 kbps | ||
| - | Yes | Yes | 192 kbps | ||
| - | No | No | 2 Mbps | ||
| Not present | Present or not | - | Yes | 192 kbps | |
| Not present | - | No | 2 Mbps | ||
| Present | - | Yes or no | 192 kbps | ||
| Not present | Present | - | Yes | - | No operation |
| - | No | - | 2 Mbps | ||
| Not present | - | - | - | 2 Mbps |
| 1The speed of serial port 1 is not affected by the
presence of a video dialing module (VDM). |
To support a T1/E1 trunk interface, your Cisco MC3810 must be equipped with a multiflex trunk module (MFT). The T1/E1 trunk port can be connected to a carrier's TDM trunk or leased lines. The MFT can transport ATM, Frame Relay, HDLC, and PPP.
The MFT is available with a balanced interface using an RJ-48 connector or with an unbalanced interface using BNC connectors. It contains a T1.403-compliant, onboard CSU/DSU.
The MFTs and their DS0 support capabilities are listed in Table 1-3. If the MFT is equipped for BRI S/T backup (even if the BRI backup is unused), the T1 and E1 trunk ports support a maximum of 22 DS0s.
Table 1-3: MFTs and DS0 Limitations | |||
| MFT Type | MFT Description | Maximum DS0s | |
|---|---|---|---|
| DS0s Terminated | DS0s Cross-connected | ||
| MFT-T1 | T1 balanced | 24 | 24 |
| MFT-E1 | E1 balanced | 24 | 30 |
| MFT-BNC | E1 unbalanced | 24 | 30 |
| MFT-TBS | T1 balanced + BRI backup | 22 | 22 |
| MFT-EBS | E1 balanced + BRI backup | 22 | 22 |
| MFT-EUS | E1 unbalanced + BRI backup | 22 | 22 |
The BRI S/T backup port makes use of a CB-1D connection with an S/T interface to the ISDN network. If an ISDN U interface is required, an external Network Termination 1 (NT1) unit must be used between the BRI S/T backup port and the U interface.
To support connectivity to a Private Integrated Services Network Exchange (PINX), a Cisco MC3810 series concentrator must be equipped with a BRI voice module (BVM) and an MFT. The BVM has four ISDN BRI S/T ports, each of which supports two voice channels (ISDN B channels). The BRI voice ports use CB-1D connections with S/T interfaces to the PINX. Direct connections between BRI voice ports and ISDN telephones are not supported. The MFT is required to support the BVM functions.
To support analog voice circuits, a Cisco MC3810 series concentrator must be equipped with an analog voice module (AVM). In its optional analog voice configuration, a Cisco MC3810 series concentrator can have up to six analog voice ports. By installing specific signaling modules known as analog personality modules (APMs), you can equip the analog voice ports for the following signaling types in various combinations: FXS, FXO, and E&M. The analog voice ports use an RJ-11 connector interface for FXS and FXO, and an RJ-1CX connector interface for E&M.
To support a T1/E1 digital voice interface, a Cisco MC3810 series concentrator must be equipped with a digital voice module (DVM). The DVM interfaces with a digital PBX, channel bank, or video codec. It supports up to 24 channels of compressed digital voice at 8 kbps, or it can cross-connect channelized data from a user's equipment directly onto the MFT for connection to a carrier network.
The DVM is available with a balanced interface using an RJ-48 connector or with an unbalanced interface using BNC connectors.
To support an RS-366 Automatic Calling Equipment (ACE) interface to video teleconferencing equipment for video dialing control, a Cisco MC3810-V or -V3 concentrator can be equipped with a video dialing module (VDM) and Cisco IOS software that supports the video dialing function. The VDM ACE port interfaces with the DTE port of the video teleconferencing equipment (server). It supports a dialing interface that carries connectivity management and encapsulation control signals for video codec dialing.
The video dialing port uses a 26-pin connector and an RS-366 ACE cable with a 25-pin D-subminiature connector on the video codec end.
The standard and optional mechanical components are in the following sections.
The basic, minimally populated Cisco MC3810 series concentrator contains the following features:
The various optional capabilities of Cisco MC3810 series concentrators are supported by replaceable functional modules. These modules, described in this section, are mounted in specific mounting locations in the chassis.
The multiflex trunk module (MFT) provides interface to a T1 or E1 trunk. Some versions provide an ISDN BRI port with an S/T interface for redundancy backup of the T1/E1 trunk port or UIO serial ports (for data traffic only), and it contains an integrated, long-haul CSU/DSU. The following MFT types are available:
The BRI voice module (BVM) provides four ISDN BRI S/T interfaces to a Private Integrated Services Network Exchange (PINX) through CB-1D ports. It supports QSIG signaling to and from the PINX. An MFT must be installed in the Cisco MC3810 chassis for the BVM to operate.
The analog voice module (AVM) provides up to six analog voice ports. Each installed voice port is supported by an analog personality module (APM). The following APMs are available to support various voice interface types and impedances:
| Note Use the show version command to view the hardware version information for APMs. |
The digital voice module (DVM)
provides a T1 or E1 interface to a PBX and contains an integrated, T1.403-compliant,
long-haul CSU/DSU. The following DVM types are available:
The video dialing module (VDM) provides an RS-366 interface to a video codec. It supports connectivity management (dialing) and encapsulation control for video teleconferencing. Because the dialing function operates across an ATM network, an MFT must be installed in the Cisco MC3810 chassis to support ATM traffic. The Cisco IOS software must be a version that supports video dialing, and the chassis must be a -V or -V3 version.
Voice compression modules (VCMs) and high-performance voice compression modules (HCMs) provide voice compression according to the voice compression coding algorithm (codec) specified when the Cisco MC3810 is configured. Table 1-4 shows the number of voice channels each type of compression module can support.
Cisco MC3810 series concentrators have internal mounting spaces for one or two compression modules, depending on the hardware configuration of the chassis. If two mounting spaces are available, any combination of one or two VCM3 and/or VCM6 modules can be installed. Likewise, one or two HCM2 and/or HCM6 modules can be installed.
| Note Do not mix VCMs with HCMs in a chassis. |
Voice compression modules have no external interfaces or cable connections.
Table 1-4: Voice Compression Module Application Information | |||
| Type | Usable in Cisco MC3810 | Codecs Supported | Maximum Voice Channels per Module |
|---|---|---|---|
| VCM3 | MC3810, MC3810-V | All codecs1, 2 | 3 of G.729 6 of other codecs |
| VCM6 | MC3810, MC3810-V | All codecs1, 2 | 6 of G.729 12 of other codecs |
| HCM2 | MC3810, MC3810-V, MC3810-V3 | All codecs1 (with codec complexity set to "high") |
4 |
| G.711, G.726, G.729a, Fax relay (with codec complexity set to "medium") |
8 | ||
| HCM6 | MC3810, MC3810-V, MC3810-V3 | All codecs1 (with codec complexity set to "high") |
12 |
| G.711, G.726, G.729a, Fax relay (with codec complexity set to "medium") |
24 |
| 1All codecs are: G.711, G.723, G.726, G.728, G.729,
G.729 Annex A and Annex B, Fax relay. 2VCM3 and VCM6 compression modules do not support codex complexity options. |
Cisco MC3810 series concentrators can be assembled in various standard hardware configurations. These are equipped with different sets of functional modules to provide specific functional capability. Many configurations are possible, but they are all variations of the basic categories described in Table 1-5. The chassis opening for any mounting area not equipped with a functional module is closed off with a removable cover plate.
Table 1-5: Cisco MC3810 Series Standard Hardware Categories | |||
| Category | Service Types Supported | Required Modules | Optional Modules |
|---|---|---|---|
| Base chassis | Base chassis services1 | None | Optional modules can be added to create other chassis variations. |
| Analog voice chassis | Base chassis services1 plus compressed analog voice connections to telephone, fax, central office, analog PBX | AVM with 1 to 6 APMs VCM3 or VCM6 or HCM2 or HCM62 |
MFT3 to support a channelized T1 or E1
trunk MFT3 and VDM4 to support video codec dialing |
| Digital voice chassis | Base chassis services1 plus compressed digital voice through digital PBX | DVM VCM3 and/or VCM62 (1 or 2 voice compression modules) |
MFT3 to support a channelized T1 or E1 trunk MFT3 and VDM4 to support video codec dialing |
| BRI voice chassis | Base chassis services1 plus compressed digital voice through PINX | BVM and MFT3 VCM3 or VCM6 or HCM2 or HCM62 |
VDM4 to support video codec dialing |
| T1/E1 trunk chassis | Base chassis services1 plus channelized T1 or E1 | MFT3 | DVM to support digital cross-connect voice (channel bank functionality/ drop-and-insert) through digital PBX or channel bank VDM4 to support video codec dialing VCM3 and/or VCM6, or HCM2 and/or HCM62, to support voice compression |
| 1Base chassis services include administrative access,
Ethernet, data transport, and video transport. 2See Table 1-4 for chassis compatibility of voice compression modules. 3The MFT is available with or without BRI backup. 4If a VDM is installed, an MFT is required to support ATM for the video dialing network connection. A VDM-compatible version of Cisco IOS software must be installed, and the chassis must be a -V or -V3 version. |
Cisco MC3810 series concentrators contain the following types of memory:
Table 1-6 summarizes the memory requirements and options.
Table 1-6: Memory Requirements and Options | |||
| Cisco MC3810 Platform | Standard Memory Combinations | Optional Memory Combinations | |
|---|---|---|---|
| MC38101, MC3810-V1 | 32 MB EDO DRAM2 8 MB Flash3 Boot ROM 17-4840-xx |
32 MB EDO DRAM2 16 MB Flash Boot ROM 17-4840-xx |
64 MB EDO DRAM2 8 MB, 16 MB or 32 MB Flash3, 4 Boot ROM 17-4840-03 or later |
| MC3810-V3 | 64 MB SDRAM 16 MB Flash5 Boot ROM 17-5270-03 or later |
64 MB SDRAM 32 MB Flash Boot ROM 17-5270-03 or later |
|
There are three power options for Cisco MC3810 series concentrators:
See Table 1-7 for power specifications.
A continuously operating cooling fan is built into the chassis.
All controls and LEDs are on the rear of the chassis. Their locations and functions are described in Figure 1-7, which shows a digital voice chassis as an example. (An analog voice chassis has no LEDs for the analog voice ports; otherwise, the LEDs are the same as those in a digital voice chassis.)
Cisco MC3810 series concentrators can be ordered with an optional NEBS Level 3/ETSI compliance kit, which contains hardware and cables to configure the -V3 digital-voice chassis for compliance with Network Equipment Business Systems (NEBS) Level 3 and European Telecommunication Standards Institute (ETSI) standards. This hardware can also be installed on the -V chassis for enhanced chassis grounding; however, NEBS Level 3/ETSI compliance is restricted to the version -V3 digital-voice chassis.
The NEBS Level 3/ETSI compliance kit contains a grounding lug, attaching hardware, 23-inch rack-mounting brackets, installation instructions, and shielded cables for the console, auxiliary, and Ethernet interfaces.
Figure 1-7: Cisco MC3810 Series Controls and LEDs
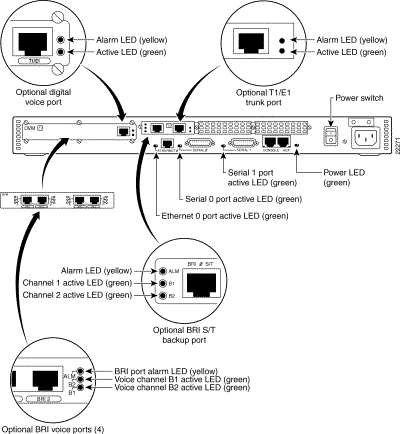
The operating system for Cisco MC3810 series concentrators is the Cisco IOS software that resides in Flash memory.
You can use an ASCII terminal or a PC to configure a Cisco MC3810 series concentrator. The configuration can be performed:
When a Cisco MC3810 series concentrator is first installed, use the procedure in
"Powering Up Cisco MC3810 Series Multiservice Access
Concentrators," for the initial configuration. This sets the
basic communication parameters. After the concentrator is operating and able to
communicate, use the procedures in the Cisco MC3810 Multiservice Access
Concentrator Software Configuration Guide to configure the specific services and
functions, or to make changes to the existing configuration.
There are several methods for configuring a Cisco MC3810 series concentrator:
Table 1-7: Cisco MC3810 Series Concentrator Technical Specifications | |
| Characteristic | Value |
|---|---|
| Dimensions (H x W x D) | 1.75 x 17.5 x 10.56 inch (44.4 x 444.5 x 268.2 mm) |
| Weight | 10 lb (4.5 kg) max. |
| Input power, AC version | 100 to 240 VAC, 1A (max.), 50 to 60 Hz, 62W (max) |
| Input power, DC version with internal DC power supply | -40 to -72 VDC, 1.5A (max), 55W (max) |
| Input power, DC version with external DC power supply (Cisco RPS) | +5 VDC, +12 VDC, -12 VDC 40W (max) |
| Main processor: In Cisco MC3810 and MC3810-V In Cisco MC3810-V3: |
40-MHz Motorola MPC860MH PowerQUICC 80-MHz Motorola MPC860P PowerQUICC |
| Operating environment | 32 to 122?F (0 to 50?C) |
| Nonoperating temperature | -40 to 185?F (-40 to 85?C) |
| Operating humidity | 5 to 95%, noncondensing |
| Noise level | 38 dB @ 3 feet (0.914 m) |
| Agency approvals | See the Cisco MC3810 Series Multiservice Access Concentrator Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information document |
| Warning Ultimate disposal of this product should be handled according to all national laws and regulations. |
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Posted: Mon Jun 26 00:18:50 PDT 2000
Copyright 1989 - 2000©Cisco Systems Inc.